Categories
ECO Friendly
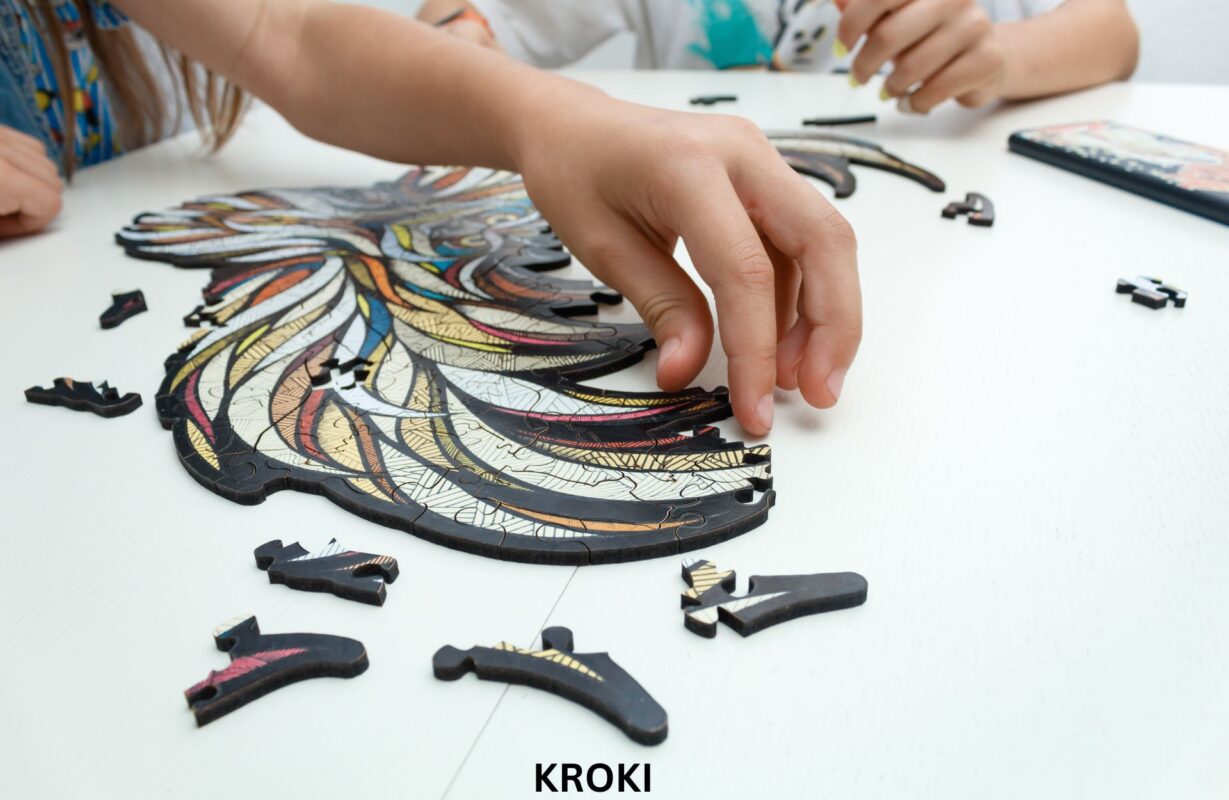
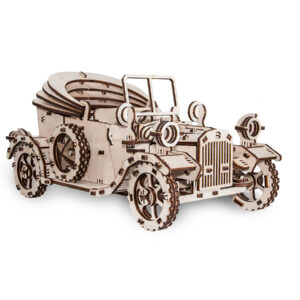
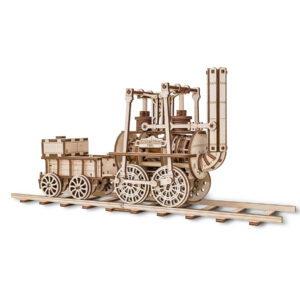
All pieces are made of natural wood. In harmony with nature.
Without Cola
Assemble hundreds of pieces without a single drop of glue.
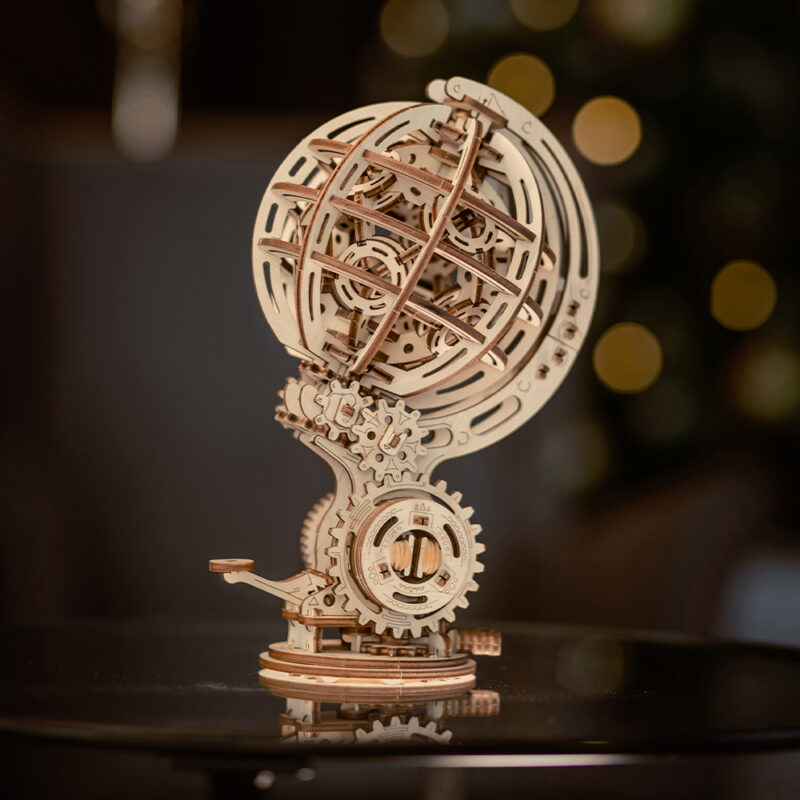
3D wooden models
Absolutely mechanical. Models come to life without batteries.